Binary Tree Approach
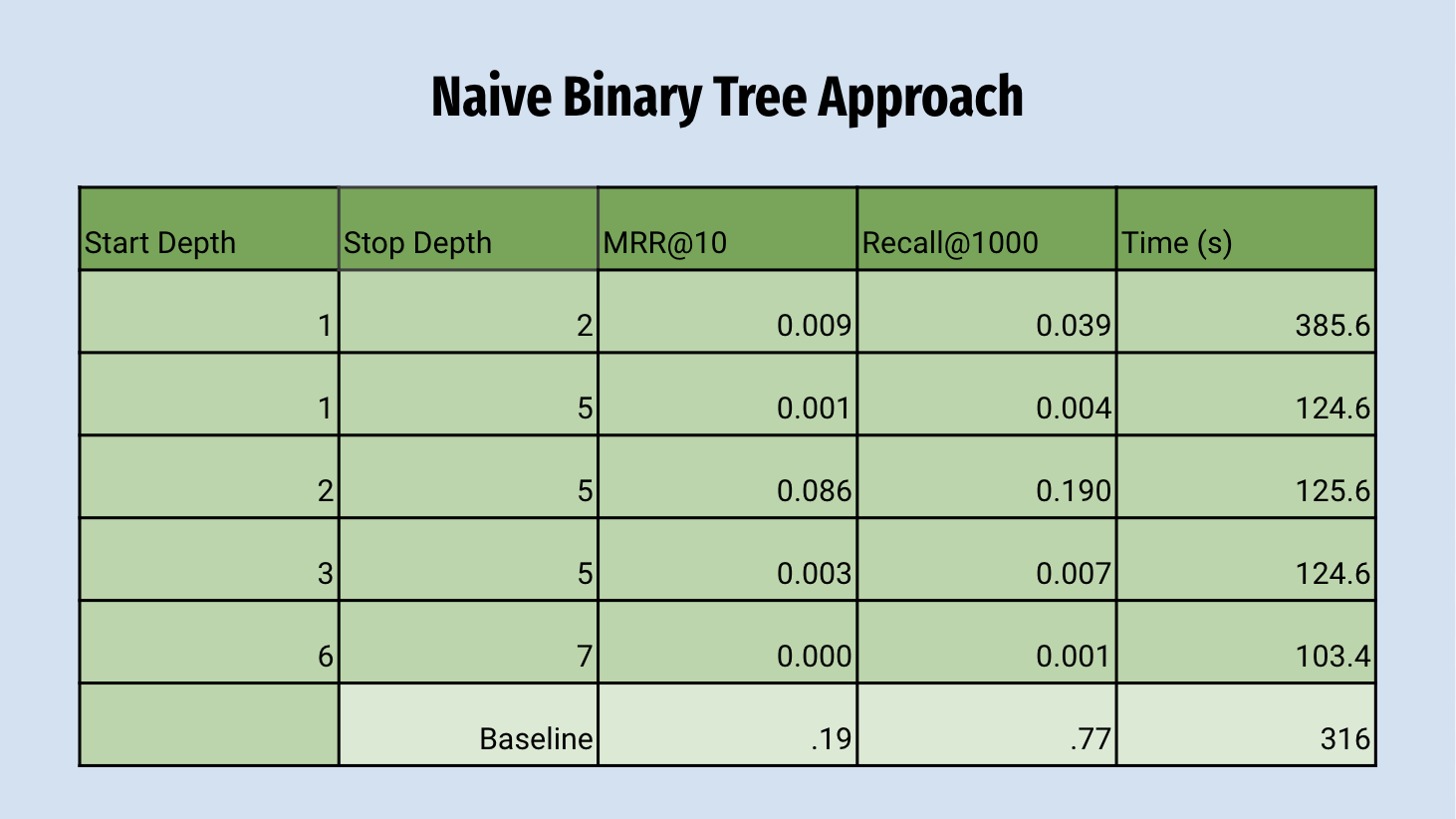
Naive Ordering:
Unfortunately, although somewhat expectedly, the Binary Tree with the Naively Ordered (unsorted)
underlying array performed very poorly
on MRR and Recall metrics. However, the retrieval time was significantly faster than the
baseline, showing some promise as a means of improving efficiency.
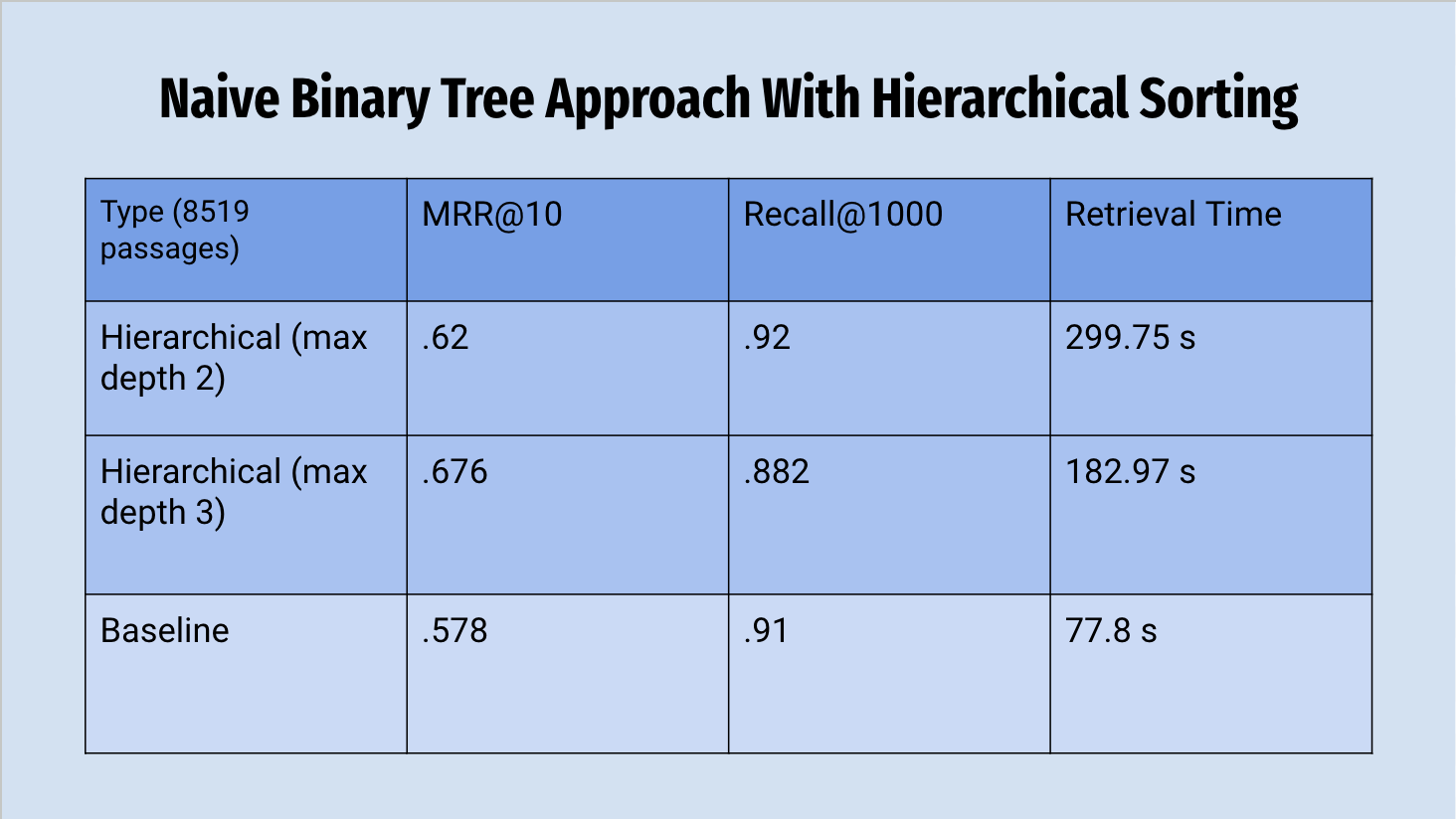
Heirarchical Odering:
The underlying array for this Binary Tree requires clustering and sorting steps. The storage
requirements for this sorting
proved to be too great for our resources, despite a modestly sized validation subset. To get
around this limitation, we used a
smaller subset of passages and queries from our validation set. While we can compare the
performance of the Binary Tree with
Hierarchical Ordering to the Baseline, it is not directly comparable to other approaches.
Because of the reduced size of the underlying array, the size of the resultant tree is much
smaller, and has fewer levels to
experiment with. Therefore, we have a single experiment to report.
As seen in the results table, the Hierarchical Ordering approach yielded promising results.
Although the retrieval time was not
competitive with that of the baseline, there is room for improvement in our implementation.
Coupled with the outperformance in MRR@10 and
Recall@1000, this may be a reasonable approach.
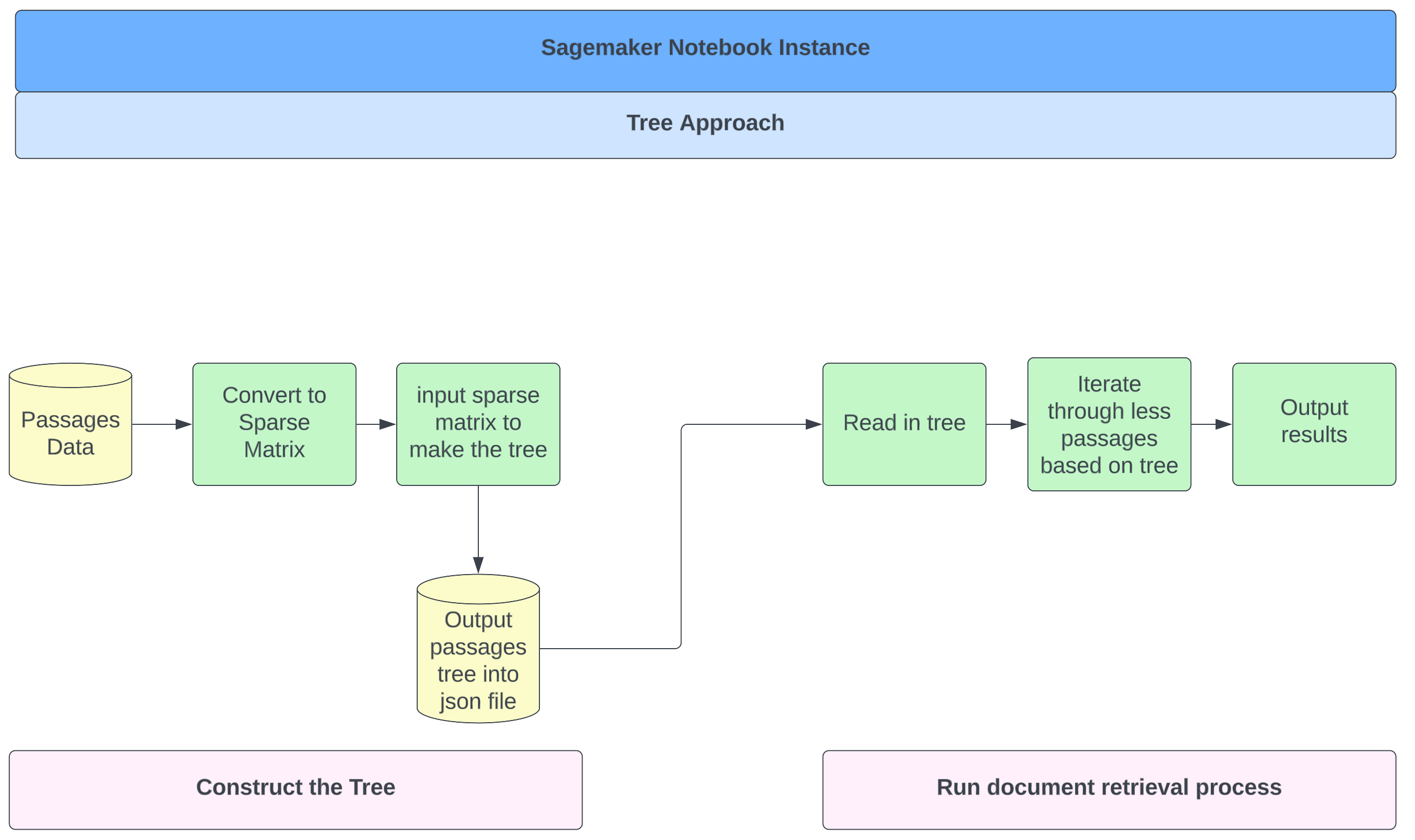
Experiments and Results